How is this drug name pronounced?
Trastuzumab: tras-TOO-zoo-mab
Herceptin: Her-SEP-tin
Herceptin was the first approved trastuzumab drug, although there are now five approved drugs that are “biosimilar” to Herceptin: Kanjinti (trastuzumab-anns), Ogivri (trastuzumab-dkst), Herzuma (trastuzumab-pkrb), Ontruzant (trastuzumab-dttb), and Trazimera (trastuzumab-gyyp). Each of these biosimilars have been shown to be similar to Herceptin in the way in which they work, how well they work, and how safe they are.
What cancer(s) does this drug treat?
Early breast cancer
Herceptin is approved for:
In such cases, Herceptin is used after surgical removal of all known disease. It may be used:
- together with doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and either paclitaxel or docetaxel chemotherapy, OR
- together with docetaxel and carboplatin chemotherapy, OR
- by itself in patients who have previously received combination chemotherapy containing anthracyclines such as doxorubicin.
Advanced breast cancer
Herceptin is approved for:
- Patients with advanced breast cancer that tests positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast and lymph nodes, and who have not received treatment for their advanced disease. In such cases, Herceptin is used in combination with the chemotherapy paclitaxel.
- Patients with advanced breast cancer that tests positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and has spread to other parts of the body, and who have received one or more chemotherapy treatments for their advanced disease. In such cases, Herceptin is used alone.
Advanced stomach cancer
Herceptin is approved for:
- Patients with gastric adenocarcinoma (stomach cancer) or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (cancer of the area where the stomach meets the esophagus) that tests positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and has spread to other parts of the body, and who have not received treatment for their advanced disease. In such cases, Herceptin is used in combination with cisplatin and capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy.
Limitations of Use:
Age: The safety and efficacy of Herceptin in patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: Treatment with Herceptin can cause serious side effects and death to a fetus. Patients should use effective contraception to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Herceptin and for at least seven months after the last dose of Herceptin. Herceptin may cause adverse reactions to a breastfed child. Women are advised not to breastfeed during treatment with Herceptin and for at least seven months after the last dose of Herceptin.
Drug interactions: Treatment with anthracycline-based chemotherapy (e.g., doxorubicin) should be avoided for up to 7 months after stopping Herceptin. Patients who receive anthracycline-based chemotherapy less than 7 months after stopping Herceptin may be at increased risk to develop heart problems.
What type of immunotherapy is this?
How does this drug work?
- Target: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)
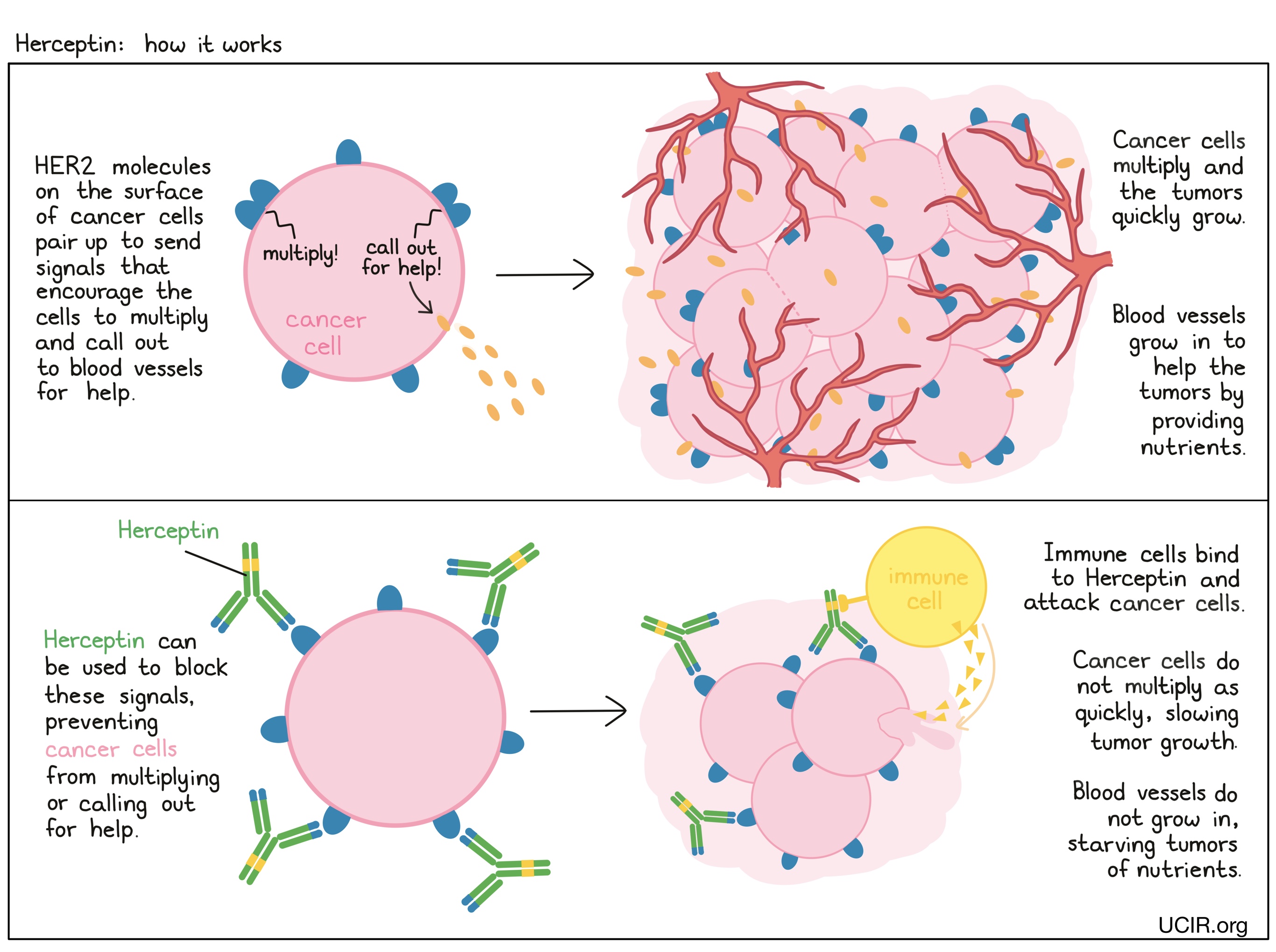
Herceptin is an antibody that was made in the laboratory and was designed to attach to a protein molecule called HER2. HER2 is present on the surface of some normal cells in the body, but is present in much higher quantities on the surface of breast and stomach cancer cells. Higher-than-normal amounts of HER2 on cancer cells make these cells the main target of Herceptin.
Herceptin and other antibody molecules have an overall “Y” shape. The two tips of the upper arms of the “Y” shape are the parts of the antibody that can very precisely bind to their target. For Herceptin, tips of the upper arms bind to HER2. The stem of Herceptin’s “Y” shape can attract immune cells or other parts of the immune system.
Hercpetin works to kill cancer cells in at least two ways.
Cancer cell growth inhibition
When HER2 on the surface of cells binds to itself or to other HER2-related proteins, it sends signals into the cell. These signals cause the cell to multiply, or in other ways promote the cell’s survival (such as causing cancer cells to produce molecules that enhance the growth of blood vessels, which help feed the tumor and support its growth). Higher-than-normal amounts of HER2 allow cancer cells to grow and multiply out of control. Binding of Herceptin to HER2 blocks HER2 from pairing up and sending these signals into the cancer cells, preventing the cells from persisting and multiplying.
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
When bound to HER2 on the surface of cancer cells, the stem of Herceptin can also attract and bind immune cells (like NK cells). This allows Herceptin to act as a bridge between the target cell and the immune cell. The immune cell then releases molecules that can kill the cell Herceptin is bound to.
How is this drug given to patients?
Before starting treatment with Hercptin, a small tumor sample is collected from a patient and is tested to determine if the tumor is positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule.
The first dose of Herceptin is administered via a tube into a vein (intravenous infusion, or i.v.) over the course of 90 minutes. Subsequent doses of Herceptin are also given by intravenous infusion, but are typically lower in amount and are delivered over the course of 30-90 minutes. Herceptin is usually administered weekly or every 3 weeks, and treatment continues out to one year, or until the cancer starts to grow again. Administration of Herceptin does not require a hospital stay. The dose and schedule for treatment with Herceptin differs slightly for the different diseases it is approved for, and may change if other drugs are part of the therapy.
Prior to the starting treatment with Herceptin, patients undergo a thorough assessment of the condition of their heart. Patients also have their hearts monitored every 3 months during treatment with Herceptin and upon completion of Herceptin treatment.
What are the observed clinical results?
For:
Early breast cancer (previously untreated after surgical removal of all known disease)
Early breast cancer (previously treated after surgical removal of all known disease)
Advanced breast cancer (previously untreated)
Advanced breast cancer (previously treated)
Advanced stomach cancer
It is important to keep in mind that each patient’s outcome is individual and may be different from the results observed in the clinical studies. In addition, with immunotherapy, it sometimes takes several months for responses to be observed.
Early breast cancer (previously untreated after surgical removal of all known disease)
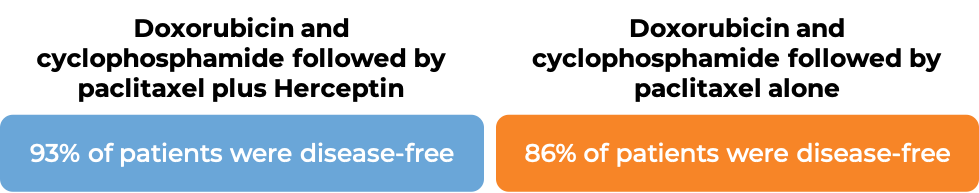
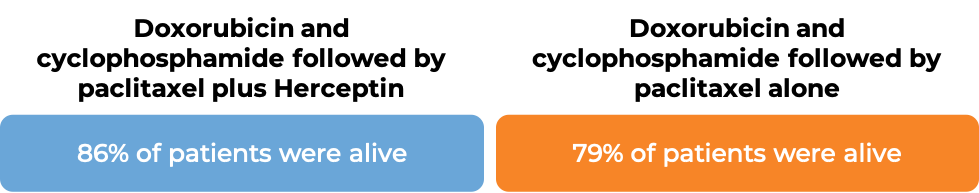
In two large clinical trials, 4063 patients with breast cancer were either treated with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy followed by paclitaxel plus Herceptin OR with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy followed by paclitaxel alone to prevent the return of disease after surgical removal of all known disease.
In an analysis of 3752 patients, at a median follow-up of 2 years:
In an analysis of 4063 patients at a median follow-up of 8.3 years:
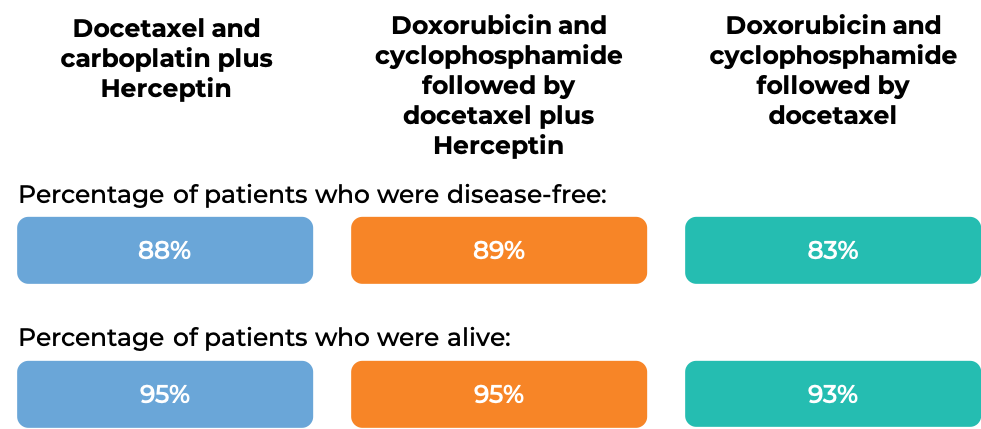
In another clinical trial, 3222 patients with breast cancer were treated with either
- Docetaxel and carboplatin plus Herceptin, OR
- Doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel plus Herceptin, OR
- Doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel
to prevent the return of disease after surgical removal of all known disease.
At the time of data analysis:
Early breast cancer (previously treated after surgical removal of all known disease)
In a clinical trial, 3386 patients with breast cancer who had already been treated with chemotherapy to prevent the return of disease after surgical removal of all known disease, were either treated with Herceptin for one or two years or were observed with no additional treatment.
At a median follow-up at 1 year:
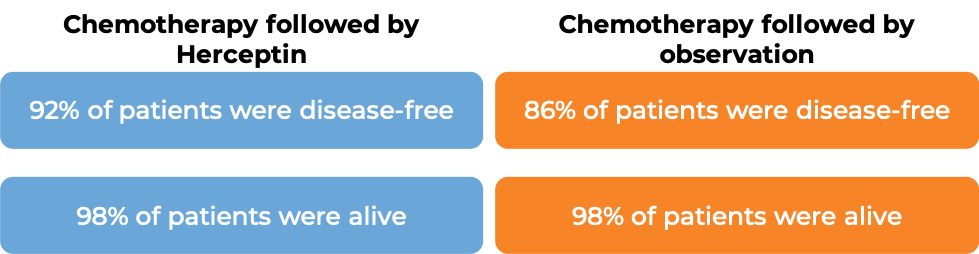
At a median follow-up of 8 years, no added benefit in treating with Herceptin for 2 years versus 1 year was found when looking at the percentage of patients who were disease-free or the percentage of patients who were alive.
Advanced breast cancer (previously untreated)
In a clinical trial, 469 patients with advanced breast cancer that tested positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and had spread to other parts of the body, and who had not been treated for their advanced disease, were treated with chemotherapy (anthracycline [doxorubicin or epirubicin] together with cyclophosphamide OR paclitaxel) plus Herceptin or chemotherapy alone.
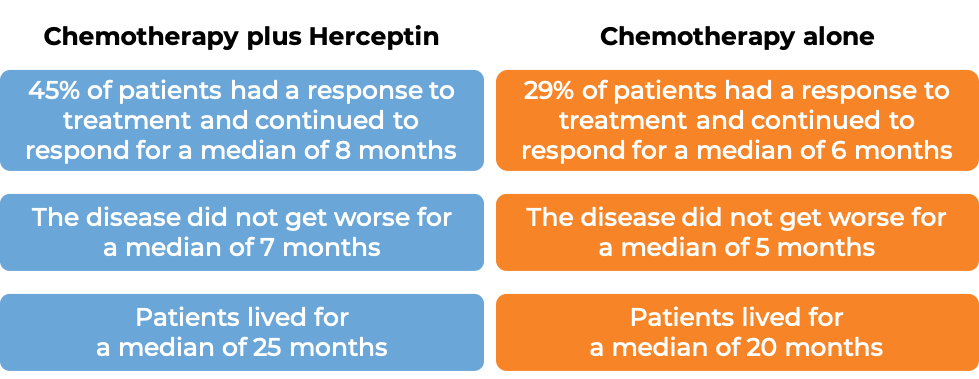
(For the definition of “median”, click HERE.)
Advanced breast cancer (previously treated)
In a clinical trial, 222 patients with advanced breast cancer that tested positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and had spread to other parts of the body, and who had been previously treated with chemotherapy, but the disease had returned, were treated with Herceptin alone. 12% of patients saw their tumors shrink and 2% of patients saw their tumors completely disappear. Complete disappearance of the tumors was only seen in patients with disease limited to skin and lymph nodes.
Advanced stomach cancer
In a clinical trial, 594 patients gastric adenocarcinoma (stomach cancer) or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (cancer of the area where the stomach meets the esophagus) that tested positive for the HER2 molecule and had spread to other parts of the body, and who had not received treatment for their advanced disease, were treated with either Herceptin plus cisplatin and capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy or with chemotherapy alone. Half the patients treated with Herceptin and chemotherapy lived for 14 months, compared with 11 months for patients treated with chemotherapy alone.
What are the side effects?
The most common side effects associated with treating breast cancer with Herceptin are: fever, nausea, vomiting, reactions to the infusion, diarrhea, infections, cough, headache, fatigue, shortness of breath, rash, low white and red blood cell count, and muscle soreness.
The most common adverse reactions associated with treating stomach cancer with Herceptin are: low white blood cell count, low platelet count, diarrhea, fatigue, irritation to mucous membranes (swelling of the lining of the mouth, nose, or throat), weight loss, upper respiratory tract infections, fever, and loss of taste.
Treatment with Herceptin in combination with chemotherapy can cause a decrease in neutrophils, a type of immune cell that helps fight infections, making patients more likely to get an infection.
Heart problems
Herceptin can cause potentially serious side effects, the most important of which is damage to the heart. Treatment with Herceptin can cause a type of heart disease in which the heart is abnormally enlarged and the heart muscle becomes thickened and/or stiffened. As a result, the heart’s ability to pump blood is less efficient. The frequency of this side effect and its severity is highest in patients receiving Herceptin together with chemotherapy containing anthracyclines, such as doxorubicin. Herceptin can also cause other heart-related problems including high blood pressure and changes to the heart’s rhythm. Prior to starting treatment with Herceptin, patients undergo a thorough assessment of the condition of their heart. Patients also have their hearts monitored every 3 months during treatment with Herceptin and upon completion of Herceptin treatment. Treatment with Herceptin will be discontinued if severe heart issues occur.
Lung problems Treatment with Herceptin can also cause serious lung side effects, including difficulty breathing, formation of scar tissue in the lungs, accumulation of some types of blood cells in the lung, accumulation of fluid around the lung, low blood oxygen levels, and more.
Infusion reactions Treatment with Herceptin can cause a set of reactions caused by the injection. The reactions may include flu-like symptoms such as fever and chills, and occasionally nausea, vomiting, pain, headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, low blood pressure, rash, and weakness. In very few patients, infusion reactions are serious and can be life-threatening; in these cases, the infusion should be immediately stopped and appropriate interventions and monitoring should be initiated. Symptoms usually occur during the infusion or within 24 hours of the infusion.
Patients should report any symptoms to their healthcare provider, who can then initiate actions to limit or reverse the side effects. For a more complete list of possible side effects, see the full prescribing information.
Manufacturer
Genentech
Approval
FDA and EMA
Links to drug websites
Last updated on March 12, 2021
How is this drug name pronounced?
Trastuzumab: tras-TOO-zoo-mab
Herceptin: Her-SEP-tin
Herceptin was the first approved trastuzumab drug, although there are now six approved drugs that are “biosimilar” to Herceptin: Kanjinti, Ogivri, Herzuma, Ontruzant, Trazimera, and Zercepac. Each of these biosimilars have been shown to be similar to Herceptin in the way in which they work, how well they work, and how safe they are.
What cancer(s) does this drug treat?
Herceptin is approved for:
Early breast cancer
Advanced breast cancer
Advanced stomach cancer
Early breast cancer
Herceptin is approved for:
- Patients with breast cancer that has spread within the breast or to the lymph nodes under the arms, but not to other parts of the body, and tests positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule.
In such cases, Herceptin is used after surgical removal of all known disease. It may be used:
- together with docetaxel and carboplatin chemotherapy, OR
- by itself, for patients who have previously received chemotherapy treatment (before or after surgery), and, if applicable, radiation therapy, OR
- together with either paclitaxel or docetaxel chemotherapy, for patients who have already received doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy after surgery.
For tumors that are more than 2 cm in diameter or are inflammatory, Herceptin is used together with chemotherapy before surgical removal of all known disease, and then again on its own after surgery.
Advanced breast cancer
Herceptin is approved for:
-
Patients with advanced breast cancer that tests positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast and lymph nodes, and who have not received treatment for their advanced disease. In such cases, Herceptin is used:
- together with docetaxel, for patients who have not yet received chemotherapy for their advanced disease, OR
- together with paclitaxel, for patients who have not yet received chemotherapy for their advanced disease and for whom treatment with chemotherapy containing anthracyclines such as doxorubicin is not an option, OR
- together with an aromatase inhibitor, for patients after menopause who have not yet been treated with a trastuzumab product (such as Herceptin) and whose cancer tests positive for hormone receptors.
-
Patients with advanced breast cancer that tests positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and has spread to other parts of the body, and who have received at least two chemotherapy treatments for their advanced disease. In such cases, Herceptin is used alone. Prior chemotherapy must have included at least one anthracycline (such as doxorubicin) and one taxane (such as paclitaxel and docetaxel), unless patients are unsuitable for these treatments. Patients whose cancer tests positive for hormone receptors must also have failed hormonal therapy, unless patients are unsuitable for these treatments.
Advanced stomach cancer
Herceptin is approved for:
- Patients with gastric adenocarcinoma (stomach cancer) or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (cancer of the area where the stomach meets the esophagus) that tests positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and has spread to other parts of the body, and who have not received treatment for their advanced disease. In such cases, Herceptin is used in combination with cisplatin and capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy.
Limitations of Use:
Age: The safety and efficacy of Herceptin in patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: Treatment with Herceptin can cause serious side effects and death to a fetus. Patients should use effective contraception to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Herceptin and for at least seven months after the last dose of Herceptin. Herceptin may cause adverse reactions in a breastfed child. Women are advised not to breastfeed during treatment with Herceptin and for at least seven months after the last dose of Herceptin.
Drug interactions: Treatment with anthracycline-based chemotherapy (e.g., doxorubicin) should be avoided for up to 7 months after stopping Herceptin. Patients who receive anthracycline-based chemotherapy less than 7 months after stopping Herceptin may be at increased risk to develop heart problems.
Exclusion: Herceptin should not be used in patients who have severe difficulty breathing or who need oxygen therapy.
What type of immunotherapy is this?
How does this drug work?
- Target: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)
Herceptin is an antibody that was made in a laboratory and was designed to attach to a protein molecule called HER2. HER2 is present on the surface of some normal cells in the body, but is present in much higher quantities on the surface of breast and stomach cancer cells. Higher-than-normal amounts of HER2 on cancer cells make these cells the main target of Herceptin.
Herceptin and other antibody molecules have an overall “Y” shape. The two tips of the upper arms of the “Y” shape are the parts of the antibody that can very precisely bind to their target. For Herceptin, tips of the upper arms bind to HER2. The stem of Herceptin’s “Y” shape can attract immune cells or other parts of the immune system.
Herceptin works to kill cancer cells in at least two ways.
Cancer cell growth inhibition
When HER2 on the surface of cells binds to itself or to other HER2-related proteins, it sends signals into the cell. These signals cause the cell to multiply or in other ways promote the cell’s survival (such as causing cancer cells to produce molecules that enhance the growth of blood vessels which help feed the tumor and support its growth). Higher than normal amounts of HER2 allow cancer cells to grow and multiply out of control. Binding of Herceptin to HER2 blocks HER2 from pairing up and sending these signals into the cancer cells, preventing the cells from persisting and multiplying.
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
When bound to HER2 on the surface of cancer cells, the stem of Herceptin can also attract and bind immune cells (like NK cells). This allows Herceptin to act as a bridge between the target cell and the immune cell. The immune cell then releases molecules that can kill the cell Herceptin is bound to.

How is this drug given to patients?
Before starting treatment with Herceptin, a small tumor sample is collected from a patient and is tested to determine if the tumor is positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule.
Herceptin is available in two different forms: one is for administration via a tube in a vein (intravenous [i.v.] infusion) and the other is for administration via an injection under the skin (subcutaneous [s.c.] injection) of the thigh. Herceptin is usually administered weekly or every 3 weeks, and treatment continues out to one year, or until the cancer starts to grow again. The first dose of Herceptin for intravenous use is administered over the course of 90 minutes. Subsequent doses of Herceptin for intravenous use are typically lower in amount and delivered over the course of 30-90 minutes. Each injection of Herceptin for subcutaneous use is given over 2-5 minutes. Herceptin for subcutaneous use additionally contains hyaluronidase, which can increase the ability of Herceptin to infiltrate into tissue under the skin and enter the bloodstream. Herceptin for subcutaneous use is not approved for the treatment of stomach cancer.
Administration of Herceptin does not require a hospital stay. The dose and schedule for treatment with Herceptin differs slightly for the different diseases it is approved for, and may change if other drugs are part of the therapy.
Prior to the starting treatment with Herceptin, patients undergo a thorough assessment of the condition of their heart. Patients also have their hearts monitored every 3 months during treatment with Herceptin and upon completion of Herceptin treatment.
What are the observed clinical results?
For:
Early breast cancer (before surgical removal of all known disease)
Early breast cancer (previously untreated after surgical removal of all known disease)
Early breast cancer (previously treated after surgical removal of all known disease)
Advanced breast cancer (previously untreated)
Advanced breast cancer (previously treated)
Advanced stomach cancer
It is important to keep in mind that each patient’s outcome is individual and may be different from the results found in the clinical studies. In addition, with immunotherapy, it sometimes takes several months for responses to be observed.
Early breast cancer (before surgical removal of all known disease)
In a clinical trial, 231 patients with breast cancer that was inflammatory or had spread within the breast or to the lymph nodes under the arms, but not to other parts of the body and tested positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule, were either treated with Herceptin and chemotherapy before surgical removal of all known disease, followed by Heceptin alone after surgery, or with chemotherapy alone before surgical removal of all known disease. (Chemotherapy consisted of treatment with doxorubicin for three treatment cycles, followed by 4 treatment cycles with paclitaxel, and 3 treatment cycles with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and fluorouracil.)
At a median follow-up of 4 years:
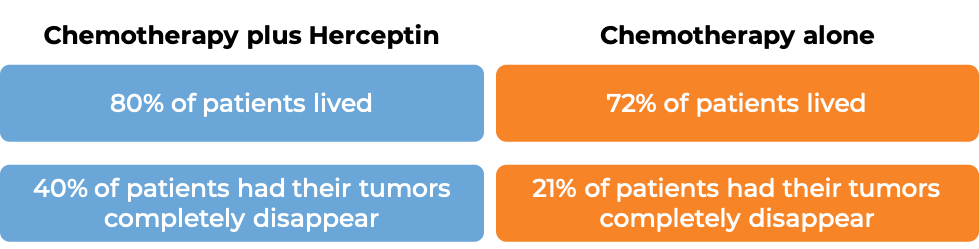
Early breast cancer (previously untreated after surgical removal of all known disease)
In two large clinical trials, 3351 patients with breast cancer were either treated with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy followed by paclitaxel plus Herceptin for intravenous use OR with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy followed by paclitaxel alone to prevent the return of disease after surgical removal of all known disease. At a median follow-up of 2 years:
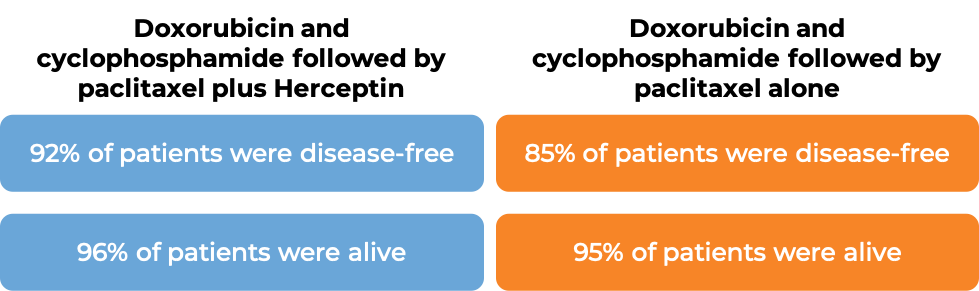
At a median follow-up of 8.3 years:

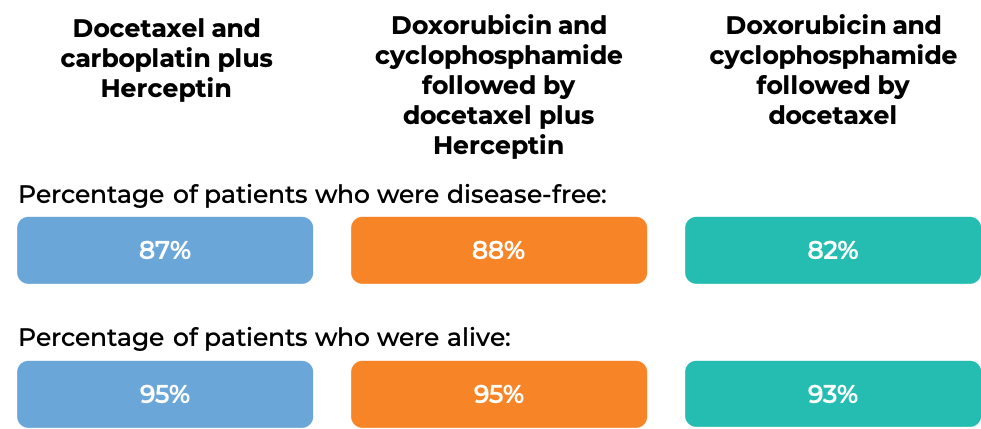
In another clinical trial, 3140 patients with breast cancer were treated with either
- Docetaxel and carboplatin plus Herceptin for intravenous use, OR
- Doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel plus Herceptin for intravenous use, OR
- Doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel
to prevent the return of disease after surgical removal of all known disease.
At a median follow-up of 3 years:
Early breast cancer (previously treated after surgical removal of all known disease)
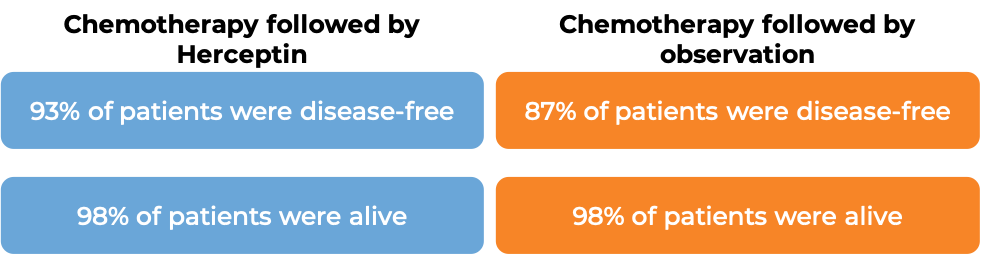
In a clinical trial, 3386 patients with breast cancer who had already been treated with chemotherapy to prevent the return of disease after surgical removal of all known disease, were either treated with Herceptin for intravenous use for one or two years or observed with no additional treatment.
At a median follow-up at 1 year:
At a median follow-up of 8 years, no added benefit in treating with Herceptin for 2 years versus 1 year was found when looking at the percentage of patients who were disease-free or the percentage of patients who were alive.
In a clinical trial, 595 patients with breast cancer that had spread within the breast or to the lymph nodes under the arms, but not to other parts of the body, or that was inflammatory, and tested positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule, were either treated with Herceptin for subcutaneous use or Herceptin for intravenous use and with chemotherapy before surgical removal of all known disease. Patients then continued treatment with Herceptin for subcutaneous use or Herceptin for intravenous use to complete 1 year of therapy. This trial was meant to compare the efficacy of Herceptin for subcutaneous use with Herceptin for intravenous use.

At a median follow-up of more than 70 months, no difference in the number of patients who were alive and had not experienced worsening of their disease was observed.
Advanced breast cancer (previously untreated)
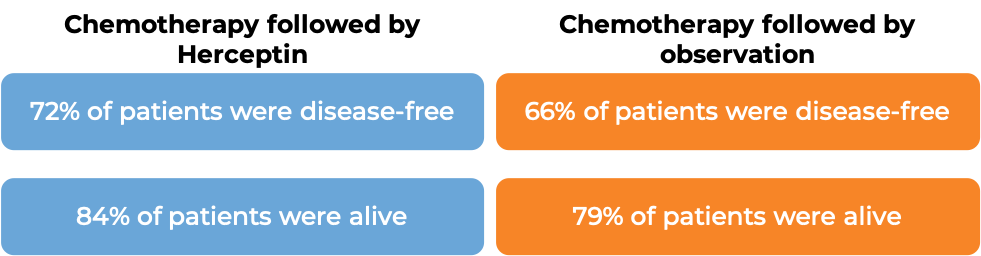
In a clinical trial, 331 patients with advanced breast cancer that tested positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and had spread to other parts of the body, and who had not been treated for their advanced disease, were treated with chemotherapy (docetaxel OR paclitaxel) plus Herceptin for intravenous use or with chemotherapy alone.
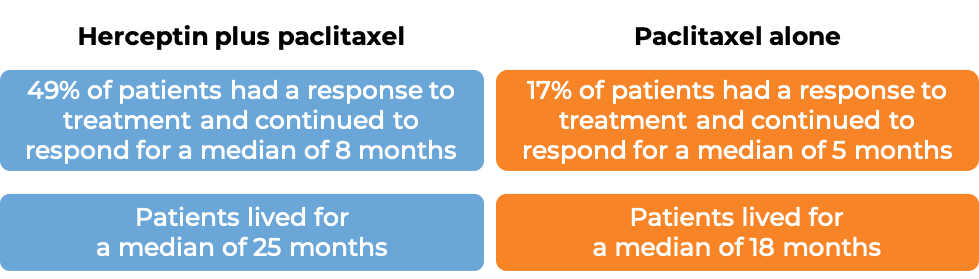
(For the definition of “median”, click HERE.)
In another clinical trial, 207 patients with advanced breast cancer after menopause that tested positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and hormone receptors and had spread to other parts of the body, and who had not been treated for their advanced disease, were either treated with Herceptin for intravenous use plus anastrozole (Arimidex) or anastrozole alone.

Advanced breast cancer (previously treated)
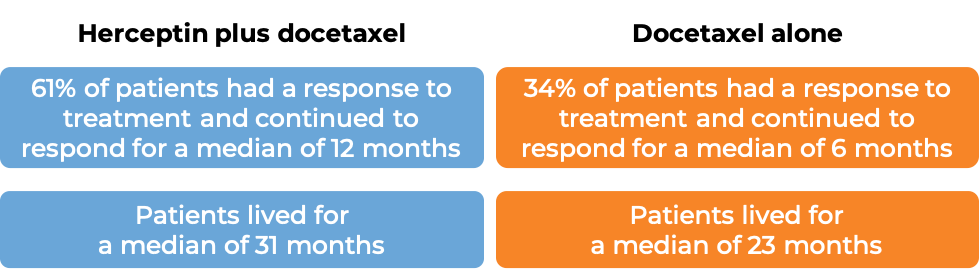
In a clinical trial, 172 patients with advanced breast cancer that tested positive for high amounts of the HER2 molecule and had spread to other parts of the body, and who had been previously treated with chemotherapy, but the disease had returned, were treated with Herceptin for intravenous use.

Advanced stomach cancer
In a clinical trial, 584 patients with gastric adenocarcinoma (stomach cancer) or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (cancer of the area where the stomach meets the esophagus) that tested positive for the HER2 molecule and had spread to other parts of the body, and who had not received treatment for their advanced disease, were either treated with Herceptin for intravenous use plus cisplatin and capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy or chemotherapy alone.
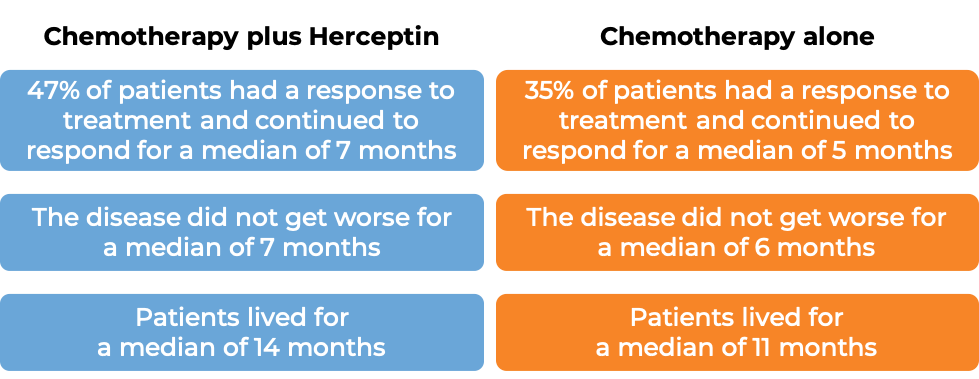
(For the definition of “median”, click HERE.)
What are the side effects?
The most common side effects associated with treating breast cancer with Herceptin are: fever, nausea, vomiting, reactions to the infusion or injection, diarrhea, infections, cough, headache, fatigue, shortness of breath, rash, low white and red blood cell count, and muscle soreness.
The most common adverse reactions associated with treating stomach cancer with Herceptin are: low white blood cell count, low platelet count, diarrhea, fatigue, irritation to mucous membranes (swelling of the lining of the mouth, nose, or throat), weight loss, upper respiratory tract infections, fever, and loss of taste.
Treatment with Herceptin in combination with chemotherapy can cause a decrease in neutrophils, a type of immune cell that helps fight infections, making patients more likely to get an infection.
Heart problems
Herceptin can cause potentially serious side effects, the most important of which is damage to the heart. Treatment with Herceptin can cause a type of heart disease in which the heart is abnormally enlarged and the heart muscle becomes thickened and/or stiffened. As a result, the heart’s ability to pump blood is less efficient. The frequency of this side effect and its severity is highest in patients receiving Herceptin together with chemotherapy containing anthracyclines such as doxorubicin. Herceptin can also cause other heart-related problems including high blood pressure and changes to the heart’s rhythm. Prior to starting treatment with Herceptin, patients undergo a thorough assessment of the condition of their heart. Patients also have their hearts monitored every 3 months during treatment with Herceptin and upon completion of Herceptin treatment. Treatment with Herceptin is discontinued if severe heart issues occur.
Lung problems
Treatment with Herceptin can also cause serious lung side effects, including difficulty breathing, formation of scar tissue in the lungs, accumulation of some types of blood cells in the lung, accumulation of fluid around the lung, low blood oxygen levels, and more.
Administration reactions
Treatment with Herceptin can cause a set of reactions caused by the infusion or injection. The reactions may include flu-like symptoms such as fever and chills, and occasionally nausea, vomiting, pain, headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, low blood pressure, rash, and weakness. In a very few patients, administration reactions are serious and can be life-threatening; in these cases, the administration should be immediately stopped and appropriate interventions and monitoring should be initiated. Symptoms usually occur during the administration or within 24 hours of the administration.
Patients should report any symptoms to their healthcare provider, who can then initiate actions to limit or reverse the side effects. For a more complete list of possible side effects, see the full prescribing information.
Manufacturer
Genentech
Approval
FDA and EMA
Links to drug websites
Other references
- Trastuzumab Plus Anastrozole Versus Anastrozole Alone for the Treatment of Postmenopausal Women With Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Positive, Hormone Receptor–Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Results From the Randomized Phase III TAnDEM Study. Kaufman et al. JCO (2009)
Last updated on August 8, 2025



















